Ecological pyramids are crucial tools for visualizing the relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem. First introduced by Charles Elton in 1927, the concept of the ecological pyramid highlights how energy, biomass, and the number of organisms are distributed across various trophic levels. This blog will delve into the three main types of ecological pyramids: the Pyramid of Numbers, the Pyramid of Biomass, and the Pyramid of Energy.
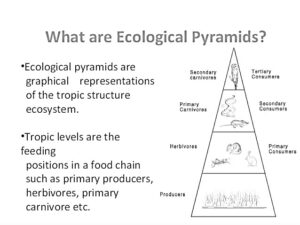
Types of Ecological Pyramids
- Pyramid of Numbers
The Pyramid of Numbers serves as a graphical representation that illustrates the relationship between producers and consumers at different trophic levels. It showcases the number of individual organisms present at each level. Generally, the base of the pyramid consists of a large number of producers, which support fewer primary consumers, followed by even fewer secondary and tertiary consumers.Upright and Inverted Pyramids:
- Upright Pyramid: In a typical ecological scenario, this pyramid shape indicates that the biomass and number of producers are significantly larger compared to consumers.
- Inverted Pyramid: However, in some ecosystems, such as those dominated by a single large producer (like a tree), the pyramid may appear inverted. In this case, a single tree supports numerous birds, while even more parasites or insects may inhabit those birds, resulting in more consumers at higher trophic levels.
- Pyramid of Biomass
The Pyramid of Biomass reflects the total mass of living matter at each trophic level. Unlike the Pyramid of Numbers, which focuses on the count of organisms, this pyramid emphasizes the weight of the biomass. Typically, producers like plants and trees form the broad base, while the biomass diminishes as one moves up to primary and secondary consumers.Example:
Consider a single tree that has a substantial biomass due to its size and structure. Above this tree, many birds (primary consumers) reside, but their collective biomass is less than that of the tree. Similarly, secondary consumers, such as hawks preying on those birds, possess an even smaller biomass. - Pyramid of Energy
The Pyramid of Energy is perhaps the most critical of the three, illustrating the flow of energy through an ecosystem. Energy pyramids always have a pyramid shape, indicating that energy decreases as it moves up through trophic levels.Energy Transfer:
For instance, if producers capture 1000 calories of energy through photosynthesis, they utilize a significant portion (about 900 calories) for their metabolic processes. This leaves approximately 100 calories for primary consumers that feed on these producers. As energy flows to secondary consumers and then to tertiary consumers, only a fraction of the energy is passed on, typically around 10% at each trophic level.
The Importance of Ecological Pyramids
Understanding ecological pyramids is essential for grasping the complexities of ecosystems. They provide a clear visual representation of the interactions and energy transfers between different trophic levels. By studying these pyramids, ecologists can assess the health and sustainability of ecosystems, making informed decisions about conservation and resource management.
In summary, the ecological pyramid is a fundamental concept in ecology that emphasizes the intricate relationships among organisms and the flow of energy and matter within ecosystems. Whether discussing the number of organisms, their biomass, or the energy they represent, ecological pyramids serve as vital tools for understanding the natural world.
For further information, visit: https://www.bing.com/
Read our previous articles: https://scitechupdate.com/super-material-could-have-more-potential-than-graphene/
Sex and Gender Studies: Unlocking Equality and Social Justice
https://scitechupdate.com/sex-and-gender-studies-unlocking-equality-and-social-justice/
Hitchhiking Aliens: New Research into Panspermia
https://scitechupdate.com/hitchhiking-aliens-new-research-into-panspermia/
The Harmful Impact of the R-Word: Why It Needs to Be Retired
https://scitechupdate.com/the-harmful-impact-of-the-r-word-why-it-needs-to-be-retired/
Social Media’s Negative Effects on Teenagers’ Brain
https://scitechupdate.com/social-media-negative-effects-teenagers-brain/
Japan’s CO2-Absorbing Concrete Home
https://scitechupdate.com/japans-co2-absorbing-concrete-home/
Utilizing Light Carbon Dioxide and Convert it into Valuable Products
https://scitechupdate.com/utilizing-light-carbon-dioxide-and-convert-it-into-valuable-products/
Scientists Pioneer Stable Efficient Next-Gen Solar Cells
https://scitechupdate.com/scientists-pioneer-stable-efficient-next-gen-solar-cells/
Einstein’s Theory Confirmed: Antigravity Challenged
https://scitechupdate.com/einsteins-theory-confirmed-antigravity-challenged/
https://scitechupdate.com/breast-cancer-in-men/
https://scitechupdate.com/scientists-proved-einsteins-emc%c2%b2-by-converting-light-into-matter/
https://scitechupdate.com/physicist-suggests-gravity-can-exist-without-mass/
https://scitechupdate.com/how-long-does-covid-19-remain-in-your-body/
Revolutionary Material Converts Sunlight and Water into Clean Fuel
https://scitechupdate.com/revolutionary-material-converts-sunlight-and-water-into-clean-fuel/
Signs of a Hidden Universe Found on the Ocean Floor
https://scitechupdate.com/signs-of-a-hidden-universe-found-on-the-ocean-floor/
Researchers find that the rate of global warming may soon decelerate
https://scitechupdate.com/researchers-find-that-the-rate-of-global-warming-may-soon-decelerate/