The Unintended Consequences of Reducing Aerosol Emissions
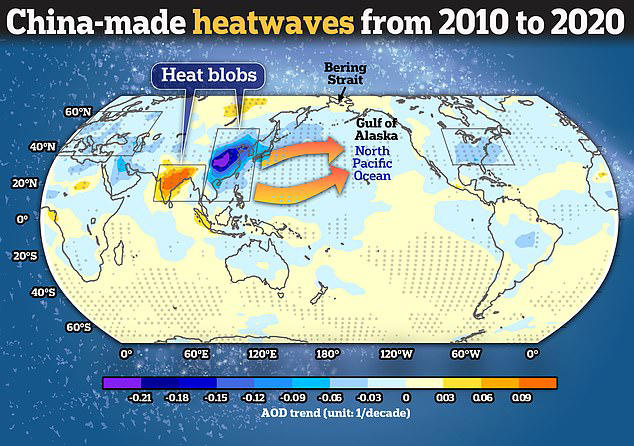
A new study from the Ocean University of China has raised concerns about the unintended consequence of reducing aerosol emissions. The study suggests that China’s efforts to cut down on aerosols, which are known to cool the Earth’s atmosphere, might be causing heat waves in the Pacific Ocean. From 2010 to 2020, the researchers observed “heat blobs” forming over the northeast Pacific, leading to ocean temperatures rising by as much as 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit. This warming trend has triggered significant ecological disruptions, including widespread fish die-offs, toxic algae blooms, and even the disappearance of whales.
The researchers linked these heat waves to China’s dramatic reduction in aerosol emissions. Typically, aerosols from industrial activities act like tiny mirrors, reflecting the sun’s heat back into space. By reducing these pollutants, China has inadvertently allowed more heat to reach the Earth’s surface, leading to increased atmospheric pressure and higher temperatures. This shift in climate patterns has sparked a debate on whether China’s approach to emission reduction needs rethinking to avoid further ecological damage.
The Impact of Heat Waves on Environment and Society
The study’s findings have broader implications, indicating a complex relationship between human activity, climate change, and environmental health. To better understand these interactions, the researchers created 12 climate models to simulate different scenarios based on varying levels of aerosol emissions. The models where aerosol emissions stayed constant showed little change in global temperatures. However, those with reduced aerosols revealed heat waves forming over the northeast Pacific.
These rising temperatures have had severe effects on both the environment and society. The weakening of the Aleutian Low, a weather system that usually brings cooler air from the Aleutian Islands into the Pacific, has led to hotter sea conditions. This shift contributed to the prolonged California drought from 2013 to 2016, causing billions of dollars in agricultural losses and the death of more than 100 million trees.
While reducing aerosols has environmental benefits, like cleaner air and fewer health risks, the study underlines the need for a balanced approach. Aerosols are also linked to serious health risks, with around eight million people dying prematurely each year from respiratory illnesses and heart disease due to aerosol-related pollution. This poses a challenge: reducing aerosols can have unintended effects on climate, but their presence also carries health risks.
Researchers stress the importance of understanding the complex dynamics between human activity and climate change. They call on governments to reassess policies on aerosol emissions, weighing the pros and cons, and considering the broader impacts on global warming and environmental health. The study is a reminder that tackling climate change requires a thoughtful, balanced approach, considering both the environmental benefits and the risks of unintended consequences.
For further Information: https://constrofacilitator.com/
Read our previous articles: First 5G-enabled Surgery performed by Doctor (scitechupdate.com)
Hitchhiking Aliens: New Research into Panspermia (scitechupdate.com)
What Is Inside the Moon? (scitechupdate.com)
Two new COVID variants, called ‘FLiRT’ in the United States (scitechupdate.com)
Sex and Gender Studies: Unlocking Equality and Social Justice (scitechupdate.com)
https://scitechupdate.com/index.php/israel-advances-cancer-treatment-with-genomic-profiling/
https://scitechupdate.com/index.php/stomach-cancer-causes-signs-and-treatment/
https://scitechupdate.com/index.php/james-webb-telescope-captures-newborn-sun-like-star/
https://scitechupdate.com/index.php/oxygen-28-unstable-magic-isotope-that-defies-expectations/







